The series of practical events organized by Datanet Systems continued in February with a laboratory dedicated to Threat Hunting operations with Cisco Security tools, a vast field that involves not only a strategic approach but also multiple cybersecurity technologies and solutions.
Supported by Bogdan Ghiţă and Cristi Marinescu, Presales consultants, the lab included theoretical presentations on the Security Operations Center (SOC)-Threat Hunting relationship and the recommended Cisco solutions, as well as a workshop on an incident investigation with Cisco Security.

Why do we need Threat Hunting
The reality shows that there are multiple organized cybercrime groups, skilled and with access to powerful technologies, that actively but discreetly work to find and exploit vulnerabilities in the IT systems of targeted organizations. Being practically impossible to cover all attack surfaces, Threat Hunting precisely aims to identify and remove attacks that have penetrated the security perimeter, without attracting attention and triggering alarms. It’s a different approach than traditional security incident investigation, which is triggered after a malicious activity is detected.
Threat Hunting operations involve multiple techniques of data mining, clustering, grouping, and stack counting, and the results are directly proportional to the data collected, the tools available, and the experience of the investigator. In Threat Hunting, the main objective is not to block the attack, for this, there are already other tools, but rather to understand the context and how an attacker or malware acts inside the network.
Through Threat Hunting, security teams discover which systems have been affected, if data has been compromised or exfiltrated, if the malware involved will resist remediation measures, or which vulnerabilities need to be fixed to avoid similar incidents in the future.
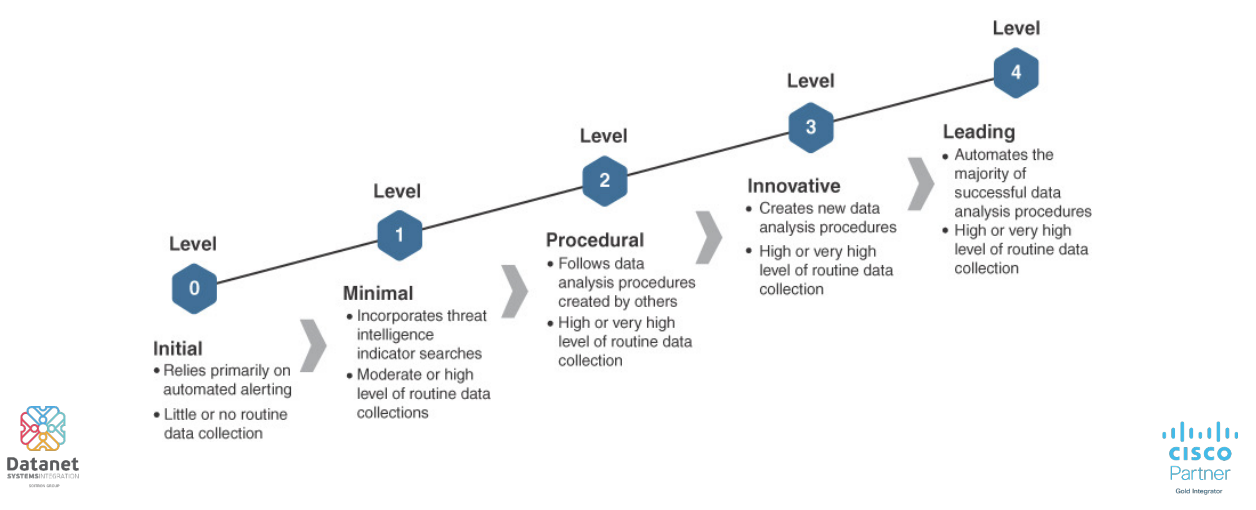
Threat Hunting operations have multiple levels of maturity, depending on the degree of routine, in terms of data collection and the level of automation of analysis procedures.
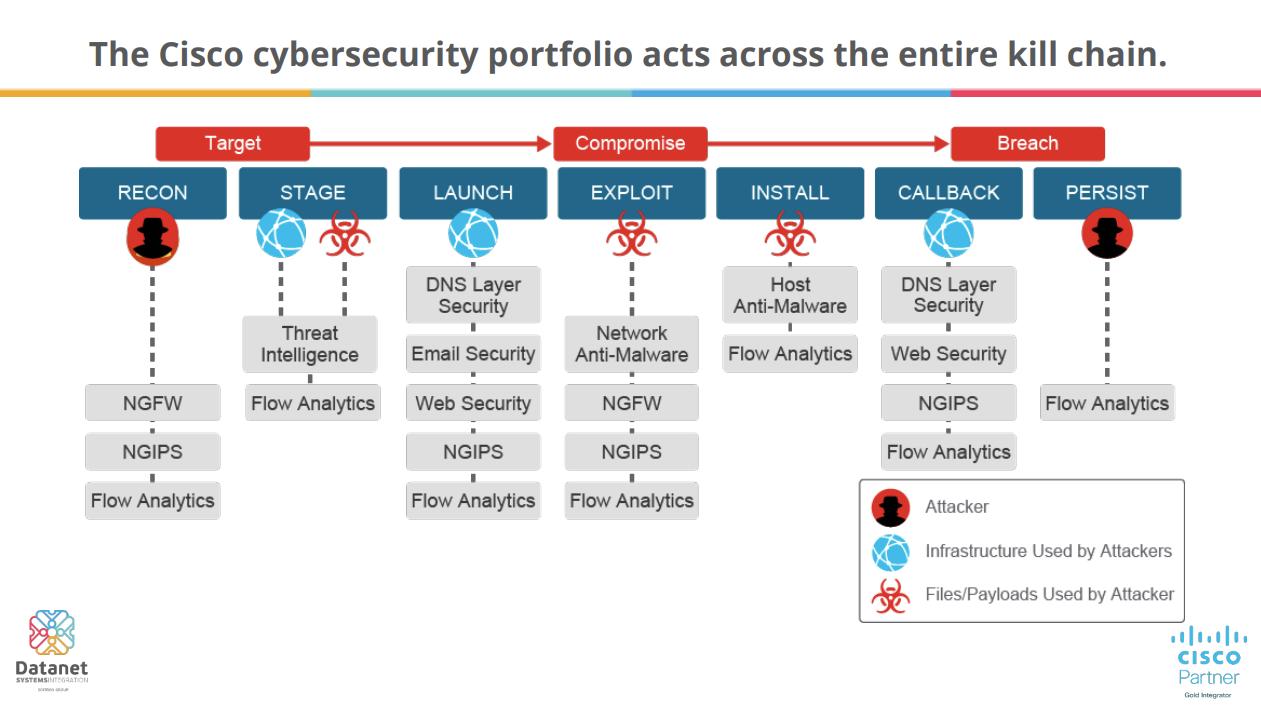
At the same time, the Threat Hunting approach differs depending on the providers. For Cisco Security, the “kill chain” flow includes several stages, each with associated specific attack and defense elements.
- Recon – attackers collect data and learn the target organization’s IT system. In the case of ransomware, phishing is the specific attack at this stage.
- Stage – the attack of malicious applications is prepared.
- Launch – the attack is launched after accessing a malicious link.
- Exploit – a device takeover vulnerability is exploited.
- Install – the actual installation of malware.
- Call Back – command flow and data encryption in case of ransomware attacks.
- Persistent – removing data from the system or blocking access to commands or data.
For each stage, Cisco offers dedicated solutions such as Secure Endpoint, Umbrella, and DUO integrated with the SecureX platform, supported by information from the Cisco Talos Intelligence Group.
One of the most used Cisco tools in Threat Intelligence scenarios is Orbital Advanced Search, a component of Cisco Secure Endpoint, available in Advantage and Premier Licenses. Orbital enables advanced queries at the endpoint level, based on a catalog of over 200 predefined queries, and, integrated with SecureX Threat Response, significantly improves response time in the event of a Threat Hunting investigation by quickly identifying affected systems.
Threat Hunting and Security Operations Center
Securitatea cibernetică este o combinație de oameni, procese și tehnologii care lucrează împreună la atingerea obiectivelor. Nici Threat Hunting nu face excepție, asigurând un nivel ridicat de eficientă atunci când este integrat într-un Security Operations Center . Why?
Because threats can be monitored more effectively when all data and security experts are grouped together and act as one. In a SOC, available services and work procedures are better documented, and resources are grouped by levels of expertise. At the same time, the advantage of a SOC resides in SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) platforms that allow an organization to collect threat data and respond to incidents without human assistance.
SOAR’s benefits:
- End-to-end orchestrated workflows
- Automated tasks by integration with various tools
- Automatic reaction to security incidents
- Metrics and performance indicators based on continuously collected data
Automation is also key in Threat Intelligence because the analyst no longer has to observe a certain situation/behavior, but the system reacts automatically by correlating several indicators. Moreover, a Security Operations Center involves the development and continuous improvement of services, and this is a Threat intelligence approach that, through retrospective analysis (facilitated by Cisco Secure Endpoint, for example), allows new decisions to be made based on information we. That is, exactly the flexibility that any organization needs to deal with today’s cyber threats.
However, beyond the theoretical approach, the main gain of participating in such an event is the involvement in practical hands-on laboratories, as being the best opportunity to understand how Cisco tools work, to get familiar with the interfaces, and especially with the work procedures. Investigating incidents with Cisco Security solutions is a complex process that requires know-how and experience, but delivers the desired results.
If you want to participate in the hands-on events organized by Datanet Systems or need information about Cisco Security contact us at sales@datanets.ro.
 6 reasons why Cisco Umbrella is the...
6 reasons why Cisco Umbrella is the...
